What is a pressure relief valve and how does it work?
A pressure relief valve is a critical component in many industries, safeguarding systems from overpressure scenarios. According to a recent report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, improper functioning of these valves can lead to catastrophic failures and severe safety hazards. Industry expert Dr. Ethan Reynolds emphasizes, “Pressure relief valves play a crucial role in protecting equipment and personnel from potentially devastating situations.”
The market for pressure relief valves has grown significantly, driven by industrial demands for safety and efficiency. Various sectors such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment heavily rely on these valves. In fact, a study from the National Institute of Standards and Technology indicated that valve failures resulted in 20% of reported industrial accidents last year. Despite their importance, many facilities still overlook regular maintenance.
Challenges exist in ensuring the reliability of pressure relief valves. They require thorough testing and monitoring, yet many organizations fail to implement proper protocols. As a result, the risk of failure can increase, impacting both safety and operational efficiency. It’s clear that understanding the function and maintenance of pressure relief valves is vital for industry professionals.
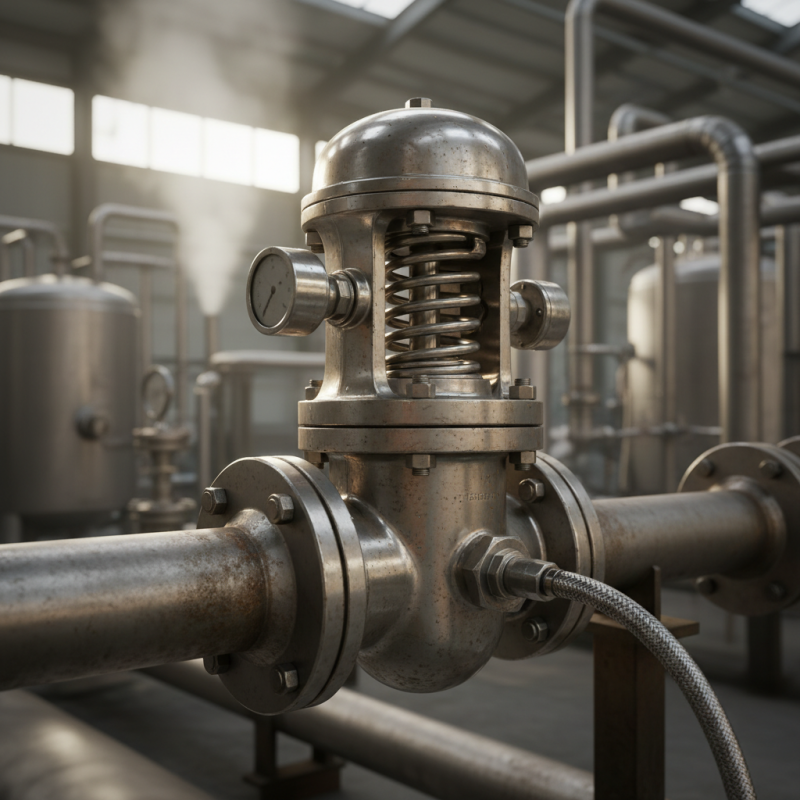

What is a Pressure Relief Valve: Definition and Purpose
A pressure relief valve is a crucial device in many systems. Its main purpose is to prevent overpressure situations that could lead to equipment failure. Designed to open under specific pressure, it allows excess fluid to escape. This action helps maintain safe operating conditions.
Understanding the functionality of pressure relief valves is essential. When the pressure exceeds a preset limit, the valve activates. It releases pressure promptly, which protects pipes and tanks. These valves can be found in numerous applications, such as boilers, gas tanks, and hydraulic systems. Their reliability is vital for safety.
However, not all pressure relief valves function perfectly. Some may fail or become stuck, leading to dangerous scenarios. Regular maintenance is important. Neglecting this can result in catastrophic failures. Ensuring proper operation is not just a routine, but a critical safety measure.
What is a Pressure Relief Valve and How Does It Work?
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A pressure relief valve (PRV) is a safety device designed to protect pressurized systems from overpressure by automatically releasing excess pressure. |
| Purpose | To prevent equipment failure, leaks, or explosions caused by excessive pressure buildup within vessels or piping. |
| Operation | PRVs operate by opening at a predetermined pressure to release fluid, thereby lowering the internal pressure to safe levels. |
| Types | Common types include spring-loaded, pilot-operated, and rupture disk valves, each suited for specific applications. |
| Applications | Used in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation, to ensure system safety. |
| Maintenance | Regular inspection and testing are essential to ensure proper functioning and compliance with safety regulations. |
Types of Pressure Relief Valves Used in Various Industries
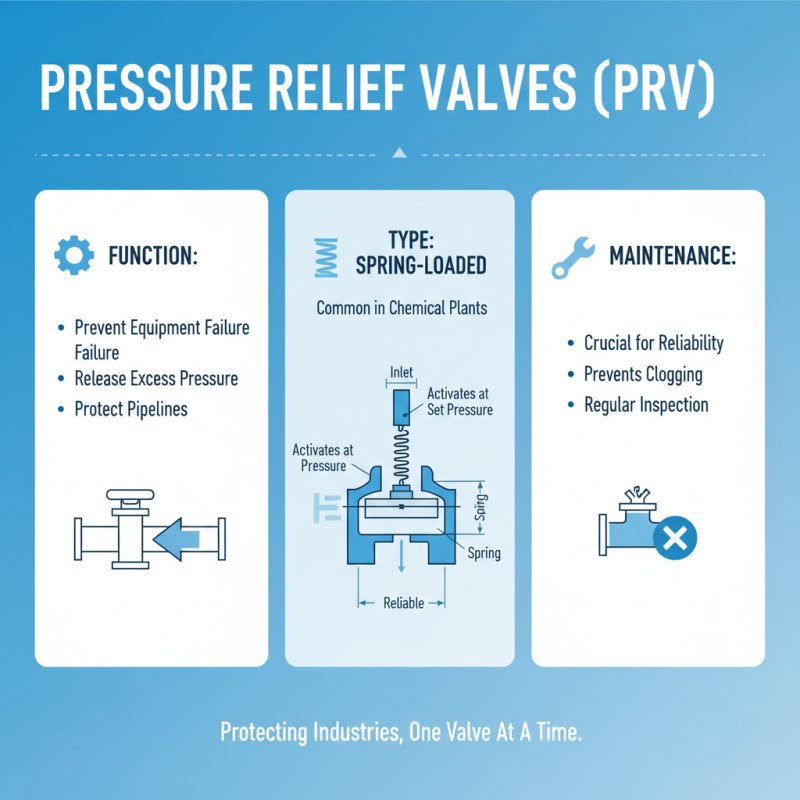
Pressure relief valves (PRVs) play an essential role in various industries by preventing equipment failure. Different types of valves cater to specific needs. For instance, spring-loaded valves are common in chemical plants. They activate at a set pressure, releasing excess pressure and protecting pipelines. They are reliable but can become clogged if not maintained properly.
Another type is the pilot-operated valve. This design uses system pressure to control flow. It’s efficient for high-pressure applications, such as power generation. However, they require regular inspections. A small malfunction can lead to significant consequences. Lastly, bursting disks are another option. These devices rupture at a certain pressure, providing a simple and effective fail-safe. While easy to use, they don’t allow for adjustments.
Selecting the right valve is crucial. Factors like pressure thresholds and fluid types must be considered. Mistakes in this selection can lead to operational issues. Industries must continuously evaluate their systems. Failure to do so can result in safety risks and expensive repairs. A proactive approach is necessary to maintain efficiency and safety in operations.
Working Principle of Pressure Relief Valves: Mechanisms and Forces
Pressure relief valves are essential components in many systems. They manage and limit the pressure within a system. When pressure exceeds a specified set point, these valves open. This action allows excess pressure to escape. As a result, it protects equipment from damage.
The working principle involves several mechanisms. Forces acting on the valve include spring tension and pressure. The spring resists pressure until it reaches a critical level. When this happens, the internal force overcomes the spring's resistance. The valve opens, releasing pressure instantly. The valve then closes when pressure drops again.
This process isn't flawless. Sometimes, valves can stick or fail. Dirt or corrosion can hinder movement. Regular maintenance is crucial for reliable operation. An unreliable valve can lead to dangerous situations. Therefore, understanding this mechanism is vital in preventing mishaps.
Applications of Pressure Relief Valves in Safety Systems and Equipment
Pressure relief valves play a crucial role in safety systems across various industries. These devices help maintain safe operating pressures in vessels or pipelines. When pressure builds beyond a safe point, the valve opens to release excess pressure, preventing potential failures. This mechanism is vital in applications like oil refineries and chemical plants.
Using pressure relief valves is not always straightforward. Improper installation or maintenance can lead to malfunction. It's essential that personnel are trained in both installation and regular checks. Often, these valves are overlooked during routine inspections, which is a mistake. It's important to regularly test them.
Tips: Always ensure that relief valves are selected based on the specific application. Each system might have unique requirements. Using a valve designed for your exact pressure range can improve safety. Also, never ignore unusual sounds or leaks. These might indicate a need for immediate attention. Regular training can prevent oversight and ensure proper functionality in emergencies.
Applications of Pressure Relief Valves in Safety Systems
Industry Standards and Regulations Governing Pressure Relief Valves
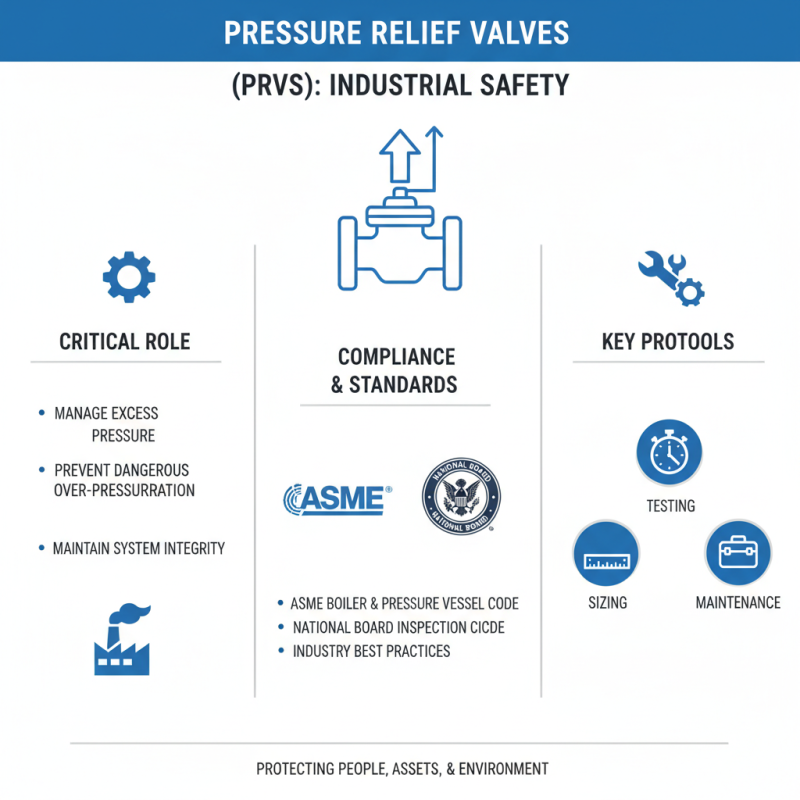
Pressure relief valves (PRVs) play a critical role in maintaining safety in various industrial applications. These valves help manage excess pressure within systems, preventing dangerous over-pressurization. Compliance with industry standards ensures their effectiveness. Key regulations come from organizations like the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors. These standards outline testing, sizing, and maintenance protocols for PRVs.
Industry reports indicate that failure to adhere to these regulations can result in costly incidents. For example, the U.S. Chemical Safety Board highlights that unregulated pressure relief systems caused severe accidents. Ensuring that PRVs are compliant not only enhances safety but also optimizes operational efficiency. Regular inspections aligned with regulatory guidelines are essential for guaranteeing proper functionality and preventing unexpected outages.
Tip: Always keep a detailed maintenance log for your pressure relief systems. Regular checks can uncover potential issues early. It’s a good idea to involve engineers in developing a comprehensive inspection schedule. Keeping up with standards can save time and costs in the long run. Being proactive is crucial; after all, occasional oversight can lead to major failures. Regular training on compliance and safety practices is also important.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Pressure Relief Valves for Optimal Safety and Performance in Industrial Applications
-

The Essential Guide to Understanding How Pressure Relief Valves Work
-

Top Strategies for Maximizing the Efficiency of Pressure Relief Valves
-

How to Choose the Right Stainless Steel Ball Valve for Your Project
-

How to Choose the Best Pressure Gauges for Your Needs in 2025
-

Why You Need a Pressure Washer for Your Home Cleaning Projects